Electric arc furnace steelmaking has a history of more than 100 years. The world's first electric arc furnace for steelmaking was invented in 1889 by Paul Héroult. The traditional electric arc furnace steelmaking process is divided into three stages: melting, oxidation, and reduction. Since there is a reduction period in the steelmaking process, it has unique advantages in smelting special steel. In the 1950s, the traditional electric arc furnace steelmaking technology developed to a mature stage. Its technical characteristics include melted oxygen merging, thin slag oxygen blowing, and shortened reduction period.

In the early 1960s, the arc continuous casting machine technology was successfully applied in production. The converter developed rapidly due to its short smelting cycle, fast production rhythm, and matching with continuous casting. This prompted the electric arc furnace smelting to develop a series of new ones focusing on shortening the smelting cycle. technology, in order to ensure that the hourly output of electric arc furnaces can adapt to the requirements of multi-furnace smelting and casting, and achieve the purpose of matching continuous casting, ultra-high-power electric arc furnaces began to emerge, and furnace wall oxygen blowing was gradually adopted to assist melting, becoming the mainstream of electric arc furnace steelmaking.
After the 1990s, due to the increase in single-strand continuous casting output, multiple strands in one machine, multi-furnace continuous casting technology and the increase in thin slab thickness, the smelting cycle was required to be further shortened. Some electric arc furnace plants in Europe and Japan developed a series of electric arc furnace smelting. Steel technology mainly includes two aspects, one is to strengthen the use of oxygen, and the other is to preheat different types of scrap steel. Various modern electric arc furnaces have emerged, and technological progress has promoted the development of electric arc furnace steel production.
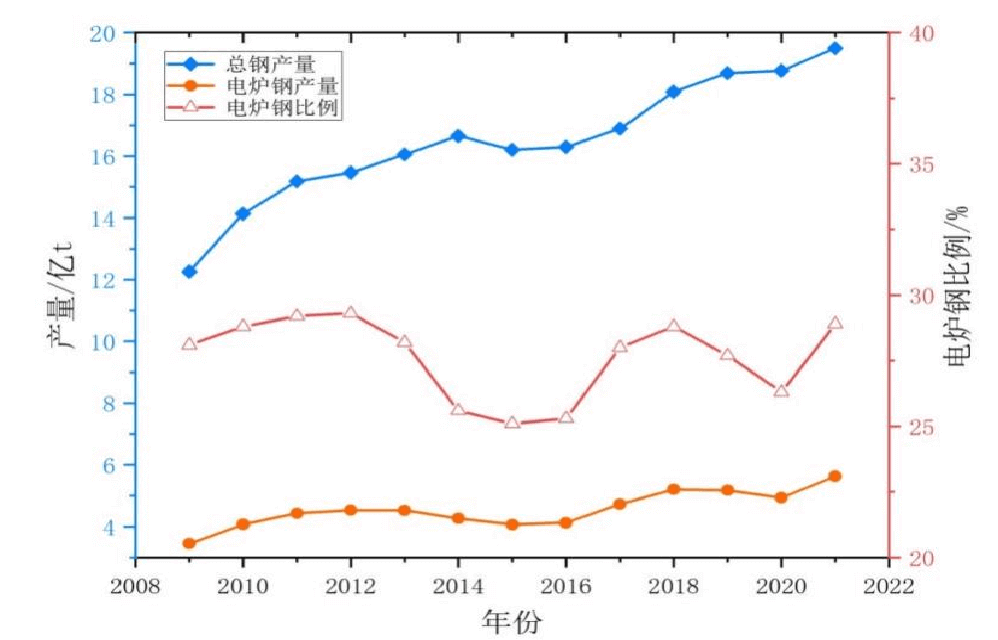
As can be seen from Figure 1-1, the world's crude steel production has been on an upward trend, reaching 1.878 billion tons in 2020, 1.951 billion tons in 2021, and 1.882 billion tons in 2022. The output of electric arc furnace steel is also increasing year by year, and the proportion of electric arc furnace steel is tortuous. rise. Among them, the proportion of electric arc furnace steel in the world declined to varying degrees from 2011 to 2015 and from 2018 to 2020. This trend is basically the same as the development trend of the proportion of electric arc furnace steel in China. The average output of electric arc furnace steel in China from 2011 to 2015 was 61.25 million tons. , which is 14.1% of the world’s average electric arc furnace steel production (434.75 million tons) during the same period; China’s electric arc furnace steel production averaged 103 million tons from 2018 to 2020, which was 2.02% of the world’s average electric arc furnace steel production (511 million tons) during the same period. %, accounting for a large proportion. Therefore, the development level of China's electric arc furnace steel affects the development level of the world's electric arc furnace steel to a certain extent.
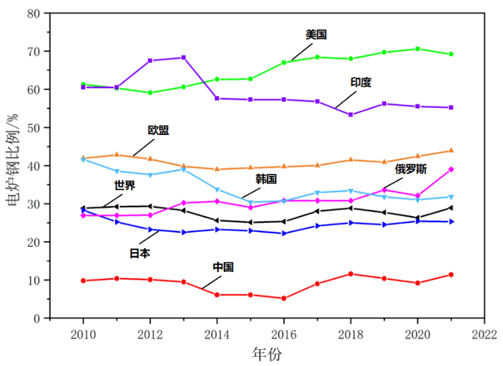
As can be seen from Figure 1-2, the overall development level of electric arc furnace steel in developed countries is relatively high. In 2010, the proportion of electric arc furnace steel in the United States exceeded 60%, and the scrap/crude steel ratio was as high as more than 70%. In 2018, the electric arc furnace steel ratio reached 68.0%. In 2022, the electric arc furnace steel ratio in the United States is 69%, the electric arc furnace steel ratio in EU countries is 43.7%, the electric arc furnace steel ratio in South Korea is 31.5%, the electric arc furnace steel ratio in Japan is 26.7%, and the electric arc furnace steel ratio in Russia is 33.1%. Even if India, a developing country, has an electric arc furnace steel level as high as 54.2%. However, the steel ratio of electric arc furnaces in my country is only about 9.5%. In 2022, China's electric arc furnace steel ratio will be 9.5%, and the world's electric arc furnace steel ratio will be 28.2%; excluding China, the average electric arc furnace steel ratio in other countries in the world will be 50.2%. Therefore, there is still huge room for China to develop short-process steelmaking.
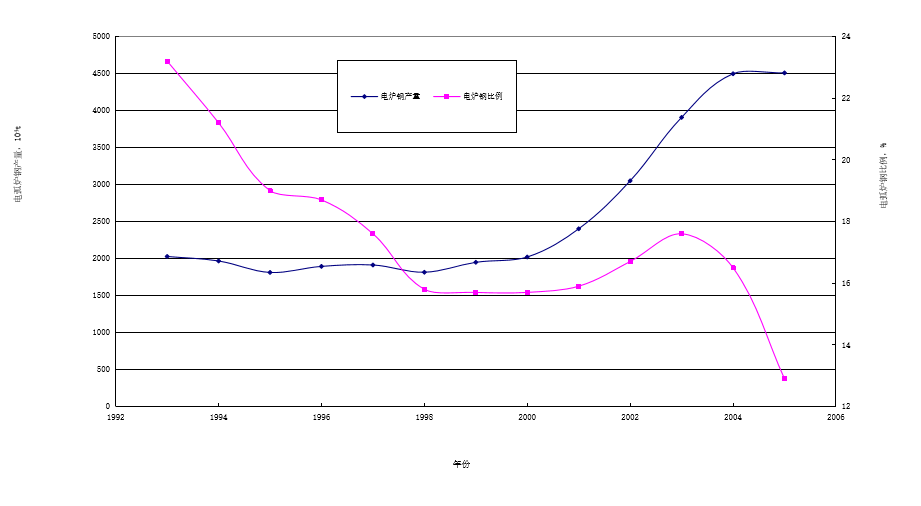
It can be seen from Figure 1-3 that the proportion of electric arc furnace steel in China was 23.2% in 1993. From 1993 to 2000, the world's electric arc furnace steel output increased. my country's electric arc furnace steel output fluctuated between 18 and 20 million tons. In 2000, the electric arc furnace steel output increased. The proportion of furnace steel dropped to 15.7%. This is due to the elimination of a large number of backward small electric arc furnaces and the low output of newly put into operation large electric arc furnaces.
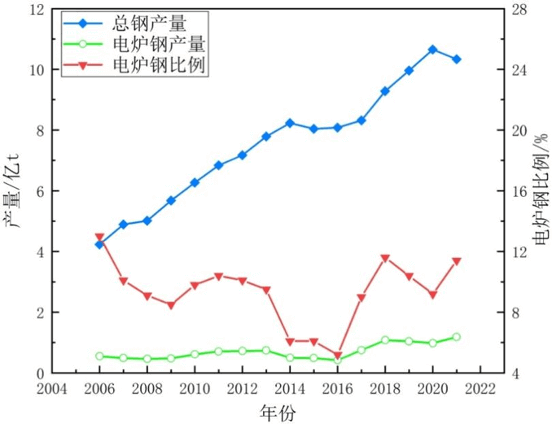
As can be seen from Figure 1-4, the proportion of electric arc furnace steel fell to the lowest point of 5.2% in 2016, which was 58.84 million tons. In 2003, China’s crude steel output was 222 million tons. Starting in 2004, crude steel output increased sharply. In 2016, crude steel output increased to 808 million tons. In 2020, China’s crude steel output reached 1.065 billion tons, accounting for 56.76% of the world's steel output.
On July 29, 2016, CCTV exposed "Strip Steel". Local governments and functional departments increased their investigation and crackdown on intermediate frequency furnaces and "Strip Steel". The price of construction steel increased, and idle electric arc furnaces Production was quickly resumed, and the "China to Electricity" project was also actively promoted, promoting the growth of electric arc furnace steelmaking output. The proportion of electric arc furnace steel continued to increase in 2017 and 2018, from 5.2% in 2016 to 9.0% in 2017. % and 11.6% in 2018. In 2019, construction steel and coke prices fell slightly, iron ore rose strongly, and supported by cost advantages, the scrap consumption of long-process steel companies increased, resulting in an increase in scrap prices and a reduction in electric arc furnace profit margins, especially due to the impact of the epidemic in early 2020. The serious backlog of finished product inventories has led to a reduction in electric arc furnace production. The proportion of electric arc furnace steel has dropped to 9.2% in 2020. The proportion of electric arc furnace steel has increased to 10.6% in 2021, while the proportion of electric arc furnace steel has dropped to 9.5% in 2022.